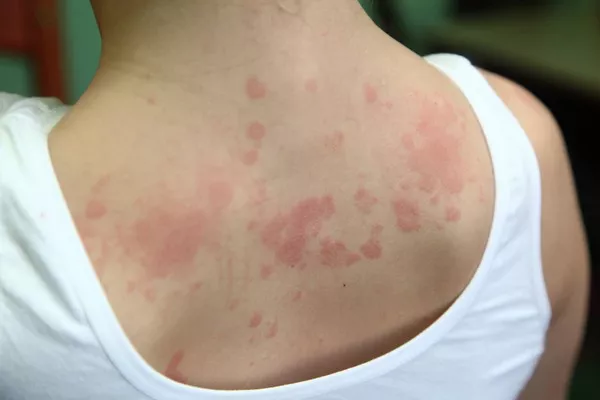
Chronic urticaria accompanied by damp-heat syndrome presents as recurrent hives lasting over six weeks, featuring unique symptoms that significantly impact patients’ quality of life. This condition combines traditional Chinese medicine concepts with Western dermatological understanding.
Key Clinical Manifestations
1. Distinctive Skin Eruptions
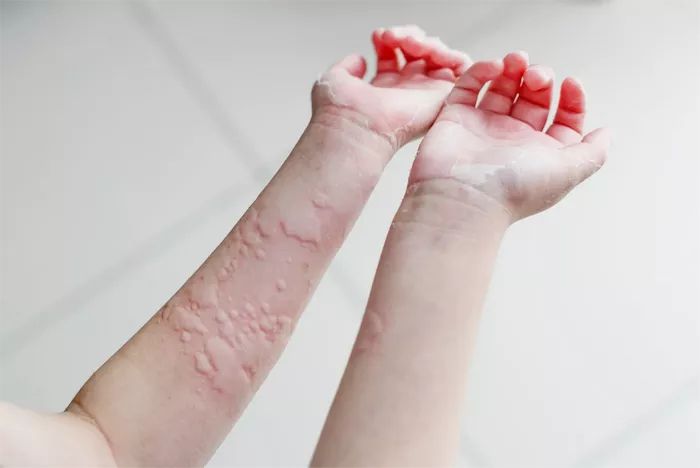
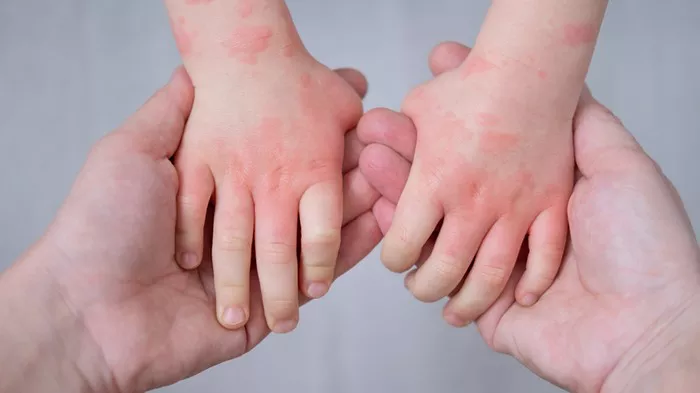
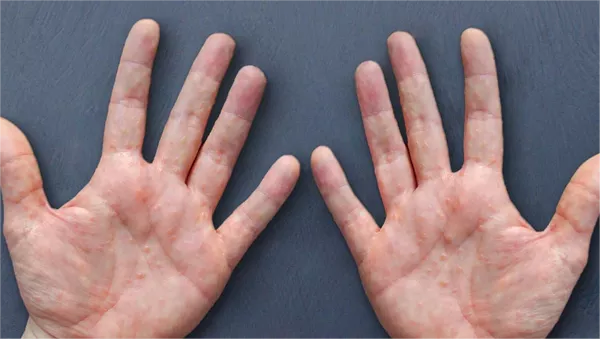
Patients experience sudden outbreaks of pink or pale wheals with clearly defined but irregular borders. These raised lesions vary in size, often merging into larger patches before disappearing within 24 hours – only to reappear in new locations. Scratching can lead to visible marks and potential secondary infections.
2. Debilitating Itching
The hallmark symptom involves intense, widespread itching that typically worsens at night, disrupting sleep patterns. What begins as localized discomfort often spreads across the body, exacerbated by heat, stress, or clothing friction. Chronic scratching may result in scaly skin and long-term pigmentation changes.
3. Vascular Involvement
About 40% of patients develop angioedema – deeper swelling in facial features or extremities. Unlike surface hives, these areas feel tight and painful rather than itchy. While rare, laryngeal swelling represents a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention.
4. Common Trigger Factors
Flare-ups frequently follow exposure to temperature extremes, emotional stress, food additives, medications, or underlying infections. The condition shows strong associations with autoimmune disorders, particularly thyroid dysfunction.
5. Unpredictable Disease Course
Symptoms follow an intermittent pattern lasting months to years. While half of patients achieve spontaneous remission within two years, a significant minority endure symptoms beyond five years, with seasonal changes and fatigue often precipitating recurrences.
Management Approaches
Experts recommend loose cotton clothing and avoidance of hot water or alcohol-based products. Keeping detailed food diaries helps identify triggers, while oatmeal baths provide soothing relief. Lifestyle modifications include maintaining regular sleep patterns and moderate (but not intense) exercise. Traditional Chinese medicine suggests incorporating diuretic foods like brown rice and red beans while avoiding seafood and spices.
When to Seek Urgent Care
While most cases can be managed with careful attention, symptoms like chest tightness, swallowing difficulty, or persistent outbreaks warrant immediate medical evaluation to prevent complications and explore advanced treatment options.
Related topic: