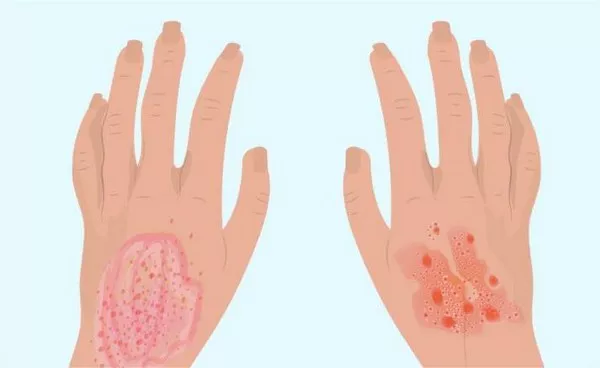
In the realm of dermatological conditions, few are as confounding and often misdiagnosed as seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. While both share some similarities in appearance and symptoms, they are distinct entities with unique underlying causes, triggers, and treatment approaches. Understanding the disparities between these two conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, elucidating their disparities and aiding in their differentiation.
Defining Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
Seborrheic dermatitis, often referred to as dandruff when affecting the scalp, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by redness, scaling, and itching. It commonly affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. The exact etiology of seborrheic dermatitis remains elusive, although factors such as Malassezia yeast overgrowth, sebum production, and immune response dysregulation are implicated.
On the other hand, psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid proliferation of skin cells, leading to the development of thick, silvery scales and inflamed, red patches. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and nails. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, and certain medications, which provoke an abnormal immune response and aberrant skin cell growth.
Clinical Presentation and Distribution
While both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis manifest as scaly, inflamed skin lesions, they exhibit distinct clinical features and distribution patterns that aid in their differentiation.
Seborrheic dermatitis typically presents as greasy, yellowish scales on an erythematous base, often accompanied by itching and burning sensations. It commonly affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, eyebrows, nasolabial folds, and central chest. The scalp involvement may result in dandruff, characterized by flaky skin and itching.
Conversely, psoriasis lesions are characterized by well-defined, raised plaques covered with thick, silvery scales. These plaques often exhibit a symmetrical distribution and commonly affect extensor surfaces, such as the elbows, knees, and lower back. In addition to the skin, psoriasis can involve the nails, causing pitting, thickening, and discoloration, a feature not typically seen in seborrheic dermatitis.
Histopathological Features
Histopathological examination plays a crucial role in distinguishing between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. While both conditions exhibit epidermal hyperplasia and inflammatory infiltrates, specific histological features can aid in accurate diagnosis.
In seborrheic dermatitis, histopathological findings include spongiosis (intercellular edema), parakeratosis (retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum), and a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate. The presence of fungal elements, such as hyphae or spores, may also be observed, reflecting the role of Malassezia yeast in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis.
In contrast, psoriasis is characterized by epidermal hyperplasia with elongation of rete ridges (acanthosis), prominent parakeratosis with neutrophilic collections (Munro’s microabscesses), and dilated blood vessels in the dermal papillae (papillary dermal vascular proliferation). The absence of fungal elements and the presence of characteristic histological features help differentiate psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis.
Differential Diagnosis and Clinical Pearls
While seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis have distinct clinical and histological features, they may sometimes overlap or be mistaken for other dermatological conditions. Differential diagnosis can be challenging, requiring a comprehensive evaluation of clinical presentation, distribution, histopathology, and response to treatment.
Other conditions that may mimic seborrheic dermatitis include allergic contact dermatitis, tinea corporis (ringworm), and pityriasis rosea. Allergic contact dermatitis presents with pruritic, erythematous patches and plaques following exposure to allergens, whereas tinea corporis manifests as annular, scaly lesions with central clearing. Pityriasis rosea presents with herald patch followed by diffuse, oval-shaped lesions along skin cleavage lines.
Similarly, psoriasis may be confused with other dermatoses, such as eczema, lichen planus, and pityriasis rubra pilaris. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, presents with pruritic, erythematous plaques with a predilection for flexural areas. Lichen planus manifests as pruritic, polygonal, flat-topped papules and plaques with a characteristic Wickham’s striae. Pityriasis rubra pilaris presents with widespread erythema and follicular hyperkeratotic papules, often involving palms and soles.
Management Strategies
Effective management of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis hinges on accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches. While both conditions are chronic and recurrent, various therapeutic modalities can alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent flare-ups.
For seborrheic dermatitis, treatment options include topical antifungal agents (e.g., ketoconazole, ciclopirox), topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., tacrolimus, pimecrolimus), and keratolytic agents (e.g., salicylic acid, sulfur). In addition to topical therapy, lifestyle modifications, such as regular shampooing with antidandruff shampoos and avoiding exacerbating factors, are integral to management.
Psoriasis management encompasses topical therapies, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologic agents, depending on the severity and extent of the disease. Topical treatments include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs (e.g., calcipotriene), and tar preparations. Phototherapy, such as narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy and psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, can effectively suppress inflammation and promote skin clearance. Systemic medications, including methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin, may be prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis refractory to topical therapy. Biologic agents, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors, interleukin-17 (IL-17) inhibitors, and interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitors, offer targeted therapy for psoriasis by modulating specific immune pathways.
Conclusion
In conclusion, seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis are distinct dermatological conditions with characteristic clinical, histological, and therapeutic features. While they share some similarities in presentation, understanding the subtle nuances and key differentiators is paramount for accurate diagnosis and optimal management. Clinicians must employ a systematic approach, integrating clinical evaluation, histopathological examination, and therapeutic interventions to effectively address seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis, thereby improving patient outcomes and quality of life.