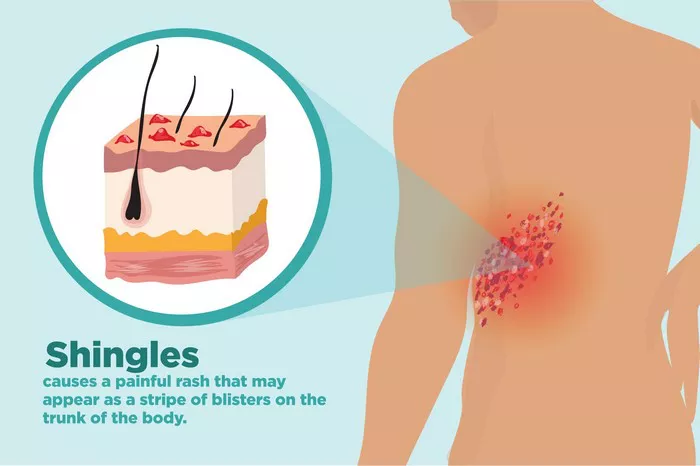
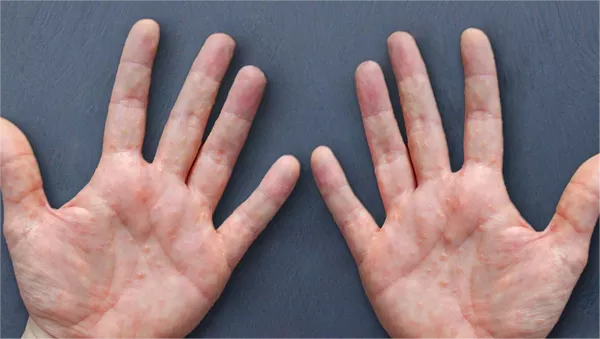
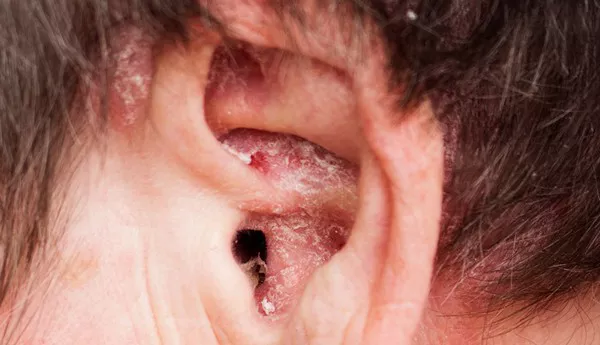
Skin allergies and itching can be managed through several methods, including cold compresses, moisturizing, oral antihistamines, topical glucocorticoids, and avoiding allergens. Common causes of skin allergies include contact allergens, food allergies, drug reactions, environmental factors, and a compromised skin barrier.
Effective Methods to Alleviate Itchy Skin
1. Cold Compress
Applying an ice pack or cold towel to the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes can help constrict capillaries, reduce inflammation, and decrease nerve sensitivity. To prevent frostbite, wrap the ice pack in a clean cloth. After cold therapy, apply a moisturizer to protect the skin barrier.
2. Moisturizing and Repairing
Use medical-grade moisturizers containing ceramides or hyaluronic acid 3 to 5 times daily. These products help restore the skin’s lipid layer and reduce irritation. Avoid skincare items with alcohol or fragrances. Opt for clinically tested dressings with medical device certifications.
3. Oral Antihistamines
Second-generation antihistamines like loratadine or cetirizine can block histamine receptors, relieving itching and redness. These medications have minimal sedative effects, making them suitable for daytime use. Always follow a doctor’s prescription, especially for individuals with liver conditions.
4. Topical Glucocorticoids
For severe inflammation, low-to-medium potency glucocorticoid creams like hydrocortisone butyrate or mometasone furoate can be used short-term. These suppress immune responses and reduce swelling. Avoid prolonged use on facial or thin skin areas, and choose milder formulations for children.
5. Avoiding Allergens
Keep a record of potential allergens such as cosmetics, detergents, or certain foods like seafood and nuts. During high-pollen seasons, limit outdoor exposure and use allergen-proof bedding. Patch tests or IgE blood tests can help identify specific triggers.
Additional Recommendations
Wear loose, breathable clothing to minimize irritation and avoid scratching to prevent infections. Maintain a balanced diet, reducing spicy or histamine-rich foods like fermented products. Indoor humidity should be kept between 40%–60%, and air purifiers can help reduce airborne allergens. Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms like difficulty breathing or facial swelling occur. Patients with chronic conditions like urticaria or eczema should schedule regular check-ups and consider immunotherapy if needed.
Related topic: