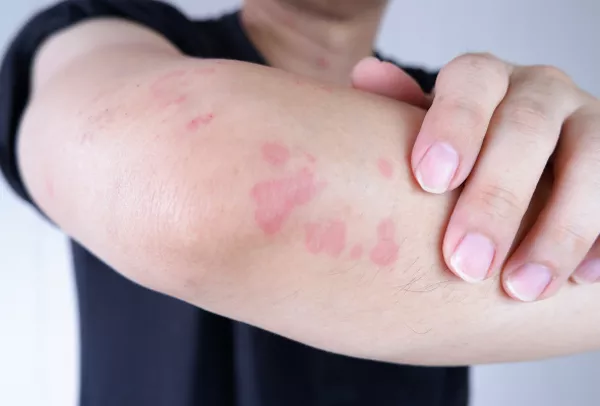
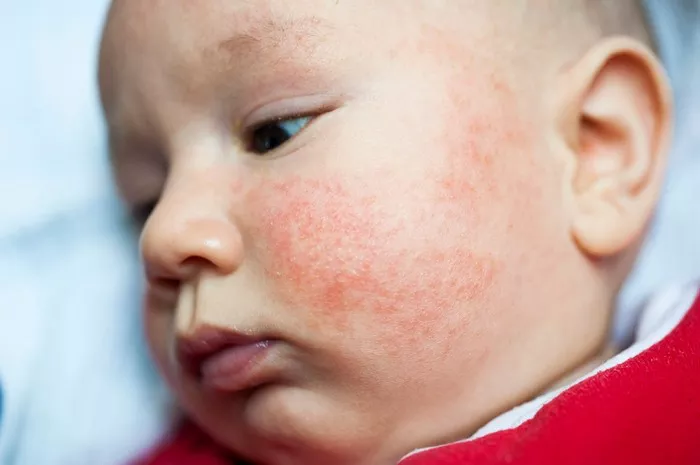
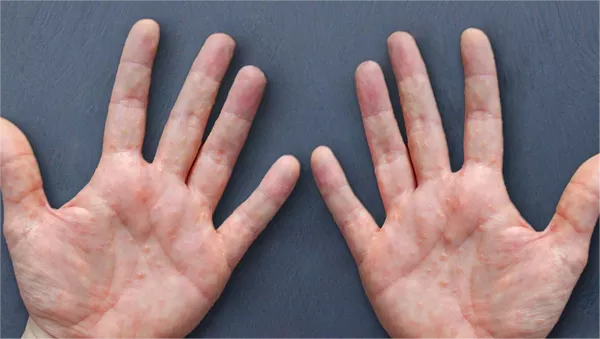
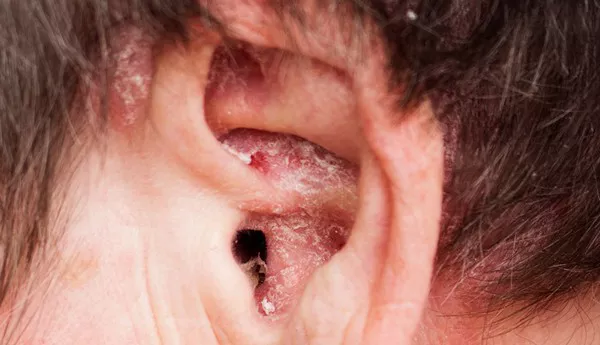
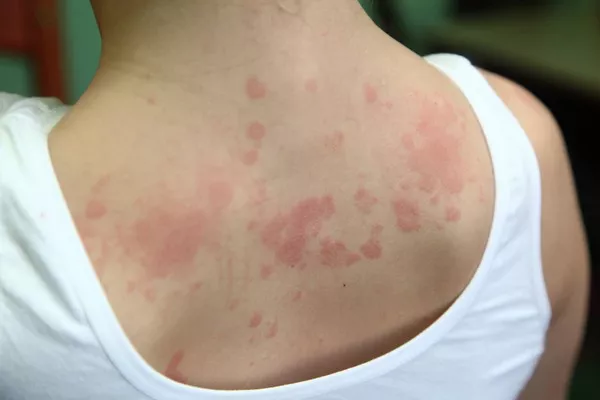
Chronic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a persistent and often debilitating skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected, often leading to discomfort, sleep disturbances, and psychological stress. Effective management of chronic eczema requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive strategies.
Understanding Chronic Eczema
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It often begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood or even begin later in life. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
Genetic Factors
Research has shown that a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever increases the likelihood of developing eczema. Genetic mutations affecting the skin barrier function, particularly in the filaggrin (FLG) gene, have been implicated in the pathogenesis of eczema. Filaggrin is a protein essential for maintaining the skin’s barrier function; mutations can lead to a compromised skin barrier, making it more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and pathogens.
Environmental Factors
Environmental triggers play a significant role in exacerbating eczema symptoms. Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and molds.
- Irritants: Soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain fabrics.
- Climate: Cold weather, low humidity, and sudden temperature changes.
- Dietary Factors: Certain foods can trigger eczema flare-ups in some individuals, such as dairy, nuts, and gluten.
- Stress: Emotional stress can worsen eczema symptoms through the release of stress hormones that affect the immune system.
Immune System Dysregulation
Eczema is associated with an overactive immune response that leads to inflammation. Individuals with eczema have a higher level of IgE antibodies, which are associated with allergic reactions. This immune dysregulation results in the release of inflammatory cytokines, contributing to the characteristic redness, swelling, and itching.
Medical Treatments for Chronic Eczema
Effective treatment of chronic eczema involves a combination of topical therapies, systemic medications, and adjunctive treatments. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, and the presence of any comorbid conditions.
Topical Therapies
Topical treatments are the cornerstone of eczema management and include:
1. Moisturizers (Emollients): Regular use of moisturizers helps to restore and maintain the skin barrier. Emollients should be applied at least twice daily and immediately after bathing to lock in moisture. Choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products to minimize irritation.
2. Topical Corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory medications used to reduce redness and itching. They are available in various strengths, from mild to potent. Long-term use should be monitored by a healthcare provider to prevent side effects such as skin thinning.
3. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors (TCIs): TCIs, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents used for sensitive areas like the face and groin. They are an alternative to corticosteroids for long-term management.
4. Topical Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) Inhibitors: Crisaborole is a newer non-steroidal topical treatment that reduces inflammation and itching by inhibiting PDE4 enzyme activity in the skin.
Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe cases of eczema that do not respond adequately to topical treatments, systemic medications may be necessary. These include:
1. Oral Corticosteroids: These are used for short-term management of severe flare-ups. Prolonged use is avoided due to significant side effects such as weight gain, osteoporosis, and increased infection risk.
2. Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine, methotrexate, and azathioprine can be used to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. Regular monitoring is essential to manage potential side effects.
3. Biologics: Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets specific pathways in the immune system involved in eczema. It is administered via injection and has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms in patients with moderate to severe eczema.
Adjunctive Treatments
Additional treatments that can help manage chronic eczema include:
1. Phototherapy: Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, particularly narrowband UVB, can reduce inflammation and itching. Treatment requires regular sessions and should be supervised by a dermatologist.
2. Wet Wrap Therapy: This involves applying a damp layer of cloth over medicated skin, followed by a dry layer. It helps to hydrate the skin and enhance the effectiveness of topical treatments.
3. Antihistamines: These can help to reduce itching, especially at night. Sedating antihistamines may also aid in improving sleep quality.
SEE ALSO: How to Treat Dyshidrotic Eczema on Fingers
Lifestyle and Home Care Strategies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle and home care strategies play a crucial role in managing chronic eczema. These strategies focus on minimizing triggers, maintaining skin hydration, and promoting overall skin health.
Bathing and Skincare Routine
A consistent bathing and skincare routine is essential for eczema management:
1. Bathing: Use lukewarm water and limit bath or shower time to 10-15 minutes. Avoid hot water, which can strip the skin of natural oils. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid harsh soaps.
2. Moisturizing: Apply a thick layer of moisturizer immediately after bathing while the skin is still damp. This helps to seal in moisture and repair the skin barrier. Choose ointments or creams over lotions, as they provide better hydration.
3. Clothing: Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid rough, scratchy materials like wool. Wash new clothes before wearing them to remove any chemical residues.
Diet and Nutrition
Dietary modifications can help some individuals manage their eczema symptoms:
1. Elimination Diet: Identify and eliminate foods that trigger eczema flare-ups. Common culprits include dairy, eggs, nuts, soy, and gluten. Work with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to ensure a balanced diet.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables can also support skin health.
Stress Management
Stress is a well-known trigger for eczema flare-ups. Effective stress management techniques include:
1. Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
2. Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes overall health and reduces stress. Choose low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling, which are less likely to irritate the skin.
3. Sleep Hygiene: Establish a consistent sleep routine and create a restful sleep environment. Use breathable bedding, keep the bedroom cool, and avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
SEE ALSO: How to Treat Painful Eczema
Avoiding Environmental Triggers
Identifying and avoiding environmental triggers is crucial for eczema management:
1. Allergen Control: Use dust mite covers on pillows and mattresses, wash bedding in hot water weekly, and keep pets out of the bedroom. Consider using air purifiers to reduce airborne allergens.
2. Climate Control: Maintain indoor humidity levels between 30-50% using a humidifier during dry weather. Avoid sudden temperature changes and protect the skin from extreme cold or heat.
Preventive Measures and Long-Term Management
Preventive measures are essential for long-term eczema management and minimizing flare-ups. These include:
Regular Follow-Up with Healthcare Providers
Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including dermatologists and allergists, are important for monitoring the condition, adjusting treatments, and addressing any concerns.
Patient Education
Educating patients and caregivers about eczema, its triggers, and management strategies empowers them to take an active role in their care. Providing written materials, resources, and support groups can be beneficial.
Skin Barrier Protection
Protecting and maintaining the skin barrier is a key preventive measure:
1. Avoiding Overwashing: Limit washing to prevent stripping the skin of natural oils. Use gentle, hydrating cleansers and avoid hot water.
2. Barrier Creams: Use barrier creams and ointments to protect the skin from irritants and allergens, especially during activities that involve frequent handwashing or exposure to harsh substances.
Early Intervention
Early intervention at the first sign of a flare-up can prevent it from worsening. This includes promptly using prescribed medications and increasing the frequency of moisturizing.
Special Considerations for Children
Eczema is common in children and requires special considerations for management:
Gentle Skincare
Use gentle, fragrance-free products designed for sensitive skin. Avoid overbathing and use mild, hypoallergenic cleansers.
Monitoring for Infections
Children with eczema are prone to skin infections due to scratching and a compromised skin barrier. Promptly treat any signs of infection, such as increased redness, oozing, or crusting, with appropriate antibiotics.
School and Social Support
Educate teachers and caregivers about the child’s condition and necessary precautions. Provide the child with tools to manage their symptoms at school, such as moisturizers and a change of clothes.
Psychological Support
Living with chronic eczema can be challenging, especially for children and adolescents. Provide emotional support and consider counseling or support groups if needed.
Conclusion
Treating chronic eczema requires a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive measures. By understanding the underlying causes and triggers of eczema, implementing effective skincare routines, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with eczema can achieve better control of their symptoms and improve their quality of life. While there is no cure for eczema, consistent and proactive management can lead to significant improvements and a more comfortable, fulfilling life.
Related Topics: