Folliculitis and seborrheic dermatitis are often confused due to their similar appearances, but they are fundamentally different skin disorders. While both conditions can cause discomfort and skin irritation, their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches vary significantly.
Different Origins of the Conditions
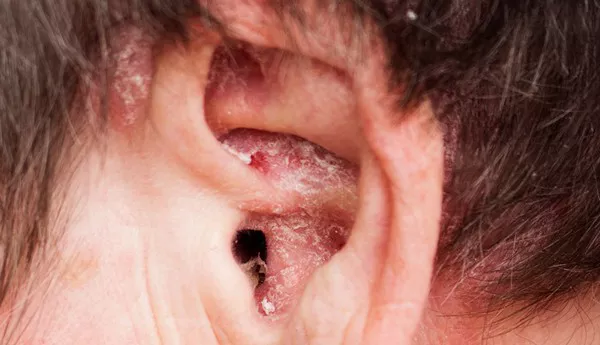
Folliculitis primarily results from bacterial infections, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. This condition typically affects areas with dense hair growth. In contrast, seborrheic dermatitis stems from an overgrowth of Malassezia fungi combined with excessive sebum production, predominantly occurring in sebaceous gland-rich regions like the scalp and face.
Recognizing the Symptoms
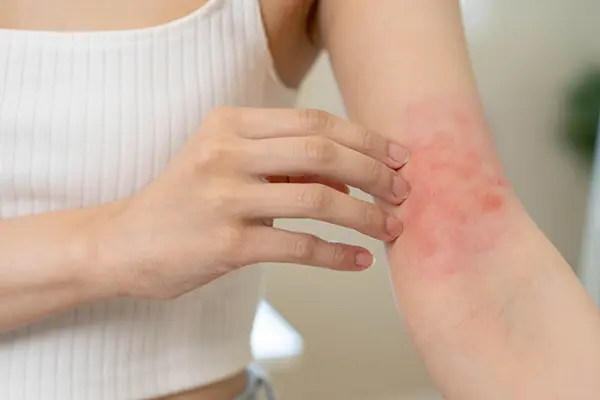
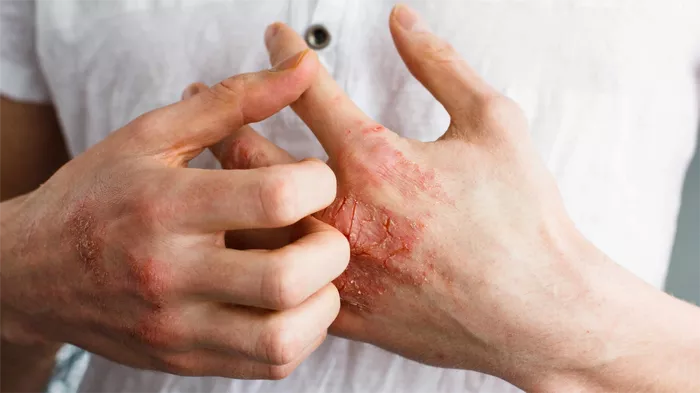
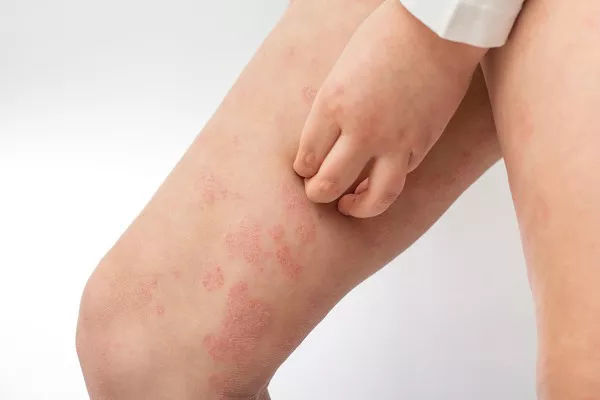
The presentation of these conditions differs markedly. Folliculitis manifests as red, swollen, and painful areas surrounding individual or multiple hair follicles, often accompanied by pustules. Seborrheic dermatitis, however, appears as red patches covered with greasy scales, frequently causing itching or burning sensations.
Treatment Approaches for Each Condition
Addressing Folliculitis
Treatment for folliculitis typically involves topical antibiotic ointments such as mupirocin or fusidic acid cream. More severe cases may require oral antibiotics to combat the infection effectively.
Managing Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis responds best to antifungal treatments like ketoconazole washes and disulfiram solutions. Topical hydrocortisone cream may also be recommended to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
Daily Care and Prevention Strategies
Folliculitis Care Recommendations
Patients should maintain excellent skin hygiene, avoid squeezing affected areas, and use gentle cleansing products. Wearing breathable clothing and keeping skin dry helps prevent recurrence.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Management
Effective management includes controlling oil production, using non-irritating skincare products, and regular scalp cleansing. Dietary adjustments, including increased intake of B vitamin-rich foods and reduced consumption of high-fat, high-sugar, and spicy foods, can significantly improve symptoms.
Lifestyle Considerations for Both Conditions
Both conditions benefit from sun protection to prevent further skin damage. Moderate aerobic exercise like walking or swimming can boost immunity and promote skin health. Patients should maintain regular sleep patterns and manage stress levels. Persistent or worsening symptoms warrant prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding these key differences enables patients to seek appropriate treatment and implement effective self-care strategies for their specific condition.
Related topic: