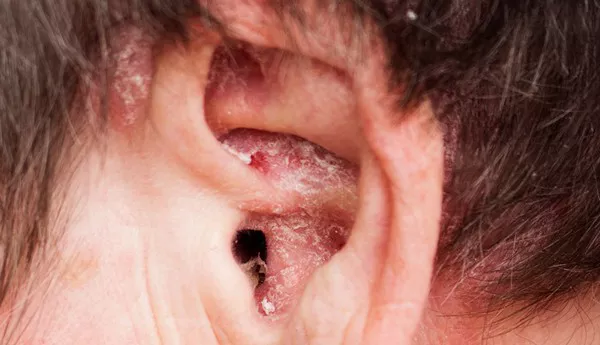
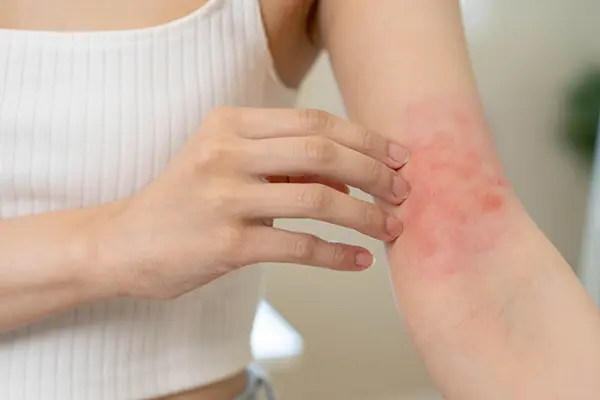
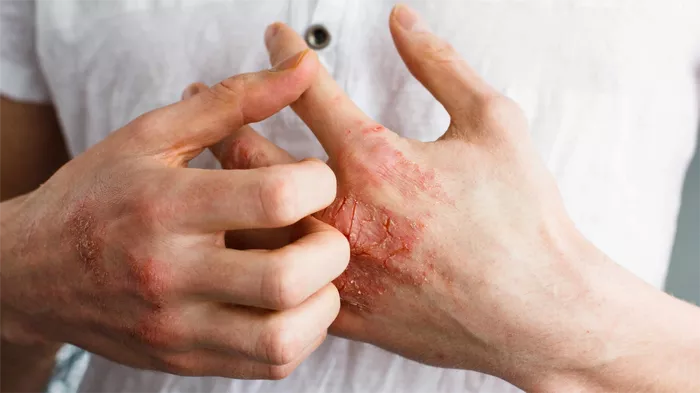
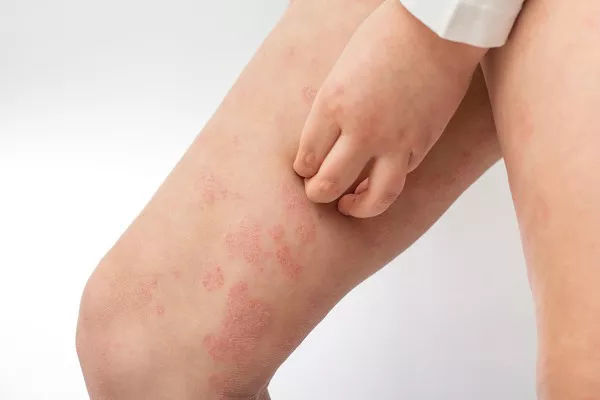
Folliculitis that persists without developing pus-filled bumps may result from bacterial infections, skin friction, or compromised immunity. When the condition remains unresolved for extended periods, it can lead to inflammation and tissue fibrosis, potentially forming hardened lesions.
Effective Treatment Approaches
Local Care Recommendations
Maintain proper hygiene by keeping affected areas clean and dry. Gentle cleansing with mild products is advised, avoiding harsh cosmetics. Warm compresses may improve circulation and reduce hardness in persistent lesions.
Medical Interventions
Topical antibiotics like mupirocin or erythromycin ointment should be applied 2-3 times daily. Oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin or cephalexin may be prescribed for 7-10 days. Severe cases might require hydrocortisone cream applications 1-2 times daily.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Daily Habits
Adequate sleep and stress management are crucial. Nutritional intake should emphasize vitamin C and zinc-rich foods like citrus fruits and nuts to support immune function.
Skin Protection Measures
Avoid prolonged exposure to humid environments and wear loose, breathable clothing to minimize skin irritation. Proper hydration and temperature regulation help prevent excessive sweating.
When to Seek Professional Help
Medical consultation is recommended if hardened lesions persist or show worsening symptoms like pain or swelling. Diagnostic procedures including skin biopsies or ultrasound examinations may be necessary to rule out other dermatological conditions.
Nutritional Support and Physical Activity
Incorporate vitamin A-rich foods such as carrots and spinach to aid skin regeneration. Regular aerobic exercise like swimming or brisk walking can enhance overall health and potentially improve skin conditions.
Related topic: