In the intricate realm of health and disease, certain symptoms can trigger a cascade of concerns and misconceptions, especially when they are linked to sensitive conditions like HIV/AIDS. One such condition that often sparks unnecessary panic is folliculitis. This seemingly common skin issue can sometimes be mistakenly associated with HIV/AIDS. This article aims to delve into the relationship between these two conditions, providing clarity and debunking myths.
Understanding Folliculitis
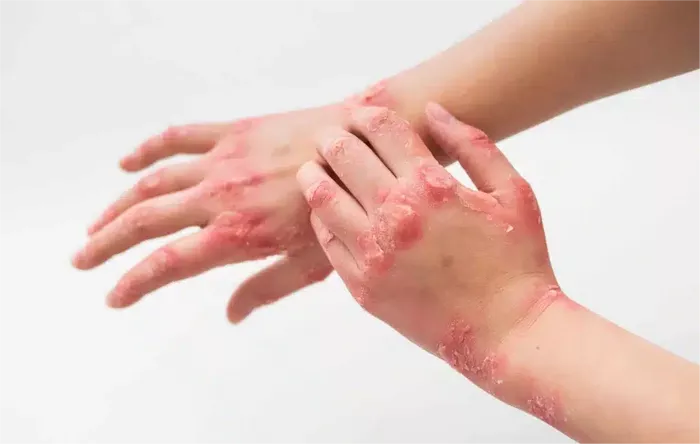
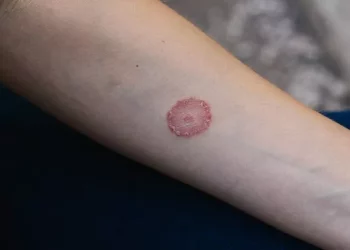
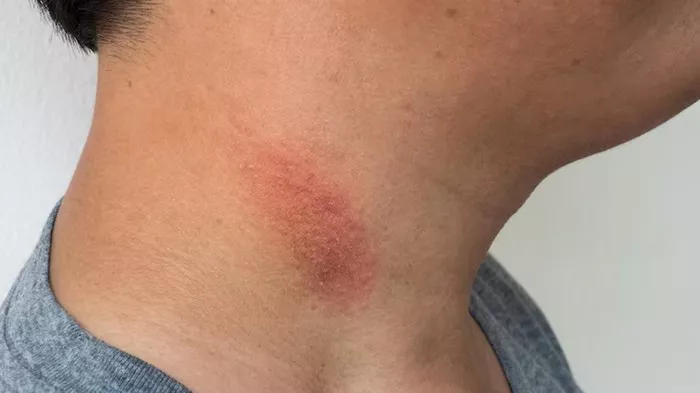
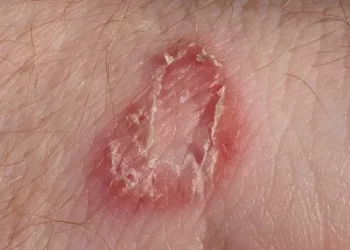
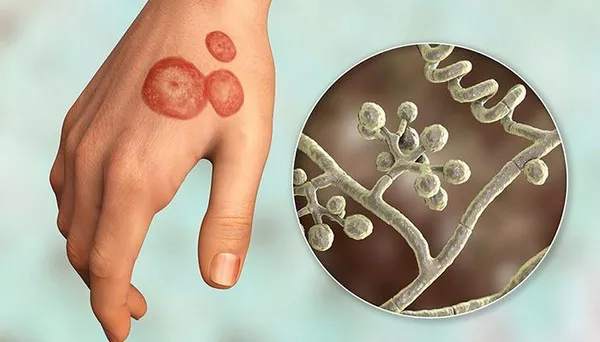
Folliculitis is essentially an inflammation of the hair follicles, typically caused by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common culprit. It can manifest anywhere on the body but is most prevalent in hair-dense areas like the scalp, neck, back, and armpits. Symptoms include red, swollen papules and pustules, often accompanied by pain and itching. In most cases, folliculitis can be effectively treated with topical antibiotic ointments or oral antibiotics, leading to a favorable prognosis.
HIV/AIDS: A Silent Immune System Collapse
HIV/AIDS, on the other hand, is a severe infectious disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). This virus specifically targets CD4+ T lymphocytes in the human immune system, which are crucial for combating foreign pathogens. As the virus replicates and CD4+ T cells diminish, the immune system progressively deteriorates, rendering the body unable to effectively fight off infections, even those caused by common bacteria or viruses.
The Misunderstanding Between HIV/AIDS and Folliculitis
While it is true that individuals with HIV/AIDS, due to their compromised immune systems, are more susceptible to various infections, including folliculitis, this does not imply that folliculitis is a direct symptom of HIV/AIDS or that its presence indicates HIV infection. In fact, folliculitis is far more common in the general population and is usually unrelated to HIV.
The key lies in understanding the indirect connection: the weakened immune system of HIV/AIDS patients makes it harder for them to resist common infections like folliculitis. Therefore, if an HIV/AIDS patient develops folliculitis, it may signal the need for further assessment and treatment of their immune status, but it does not mean that all individuals with folliculitis should worry about HIV infection.
A Scientific Approach to Prevention and Treatment
To address the misconceptions surrounding HIV/AIDS and folliculitis, it is crucial to maintain a scientific perspective. For folliculitis, maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding excessive scratching, and using appropriate antimicrobial medications are key to treatment. For HIV/AIDS prevention, emphasis should be placed on safe sexual practices, avoiding sharing needles, and seeking proper medical care.
Moreover, for any health concerns, especially those involving infectious diseases, consulting a healthcare professional and undergoing necessary tests is the wisest course of action, rather than relying on unverified information from the internet.
In summary, while there may be some overlap in the health issues faced by individuals with HIV/AIDS and those with folliculitis, they are largely distinct health concerns. By adopting a scientific understanding and implementing reasonable preventive measures, we can better protect ourselves and others from the burden of disease.
Related topics
<“answer-action-bar-wEWc6C bottom-action-bar-wrapper-qtqrci large-space-b582O0 answer-action-bar” data-testid=”message_action_bar”>
<“container-seCXVJ container-TRt1mF bottom-action-bar-iUQiGg”>
<“left-Qpwvoi”>
<“bp5-overflow-list container-LFxhPL align-start-B2LgK_ inner-TjQIQn”>